Chapter 8: Light, Shadows, and Reflections
Introduction to Light
What is Light?
Light is a form of energy that enables us to see the world around us. It travels in straight lines and can come from natural sources like the sun or artificial sources like bulbs and torches.
Importance of Light
Light is essential for vision. Without light, we would not be able to see anything. It also plays a crucial role in the process of photosynthesis in plants.
Transparent, Translucent, and Opaque Objects
Definition and Examples
Transparent objects allow light to pass through them completely, e.g., clear glass, clean water.
Translucent objects allow some light to pass through them, e.g., frosted glass, wax paper.
Opaque objects do not allow any light to pass through them, e.g., wood, metal.
Characteristics of Each Type
Transparent objects are clear and allow us to see through them. Translucent objects are partially clear, making objects behind them appear blurred. Opaque objects block light completely, creating shadows.
Shadows
Formation of Shadows
Shadows are formed when an opaque object blocks the path of light. To form a shadow, you need a light source, an opaque object, and a surface where the shadow will be cast.
Characteristics of Shadows
Shadows are always formed on the opposite side of the light source. The size and shape of a shadow depend on the angle and distance of the light source. Closer the object to the light source, larger the shadow.
Reflection of Light
What is Reflection?
Reflection occurs when light bounces off a surface. This is why we can see ourselves in mirrors. Smooth, shiny surfaces like mirrors reflect light well.
Applications of Reflection
Mirrors: Used in daily life for grooming and decoration.
Periscope: A device used in submarines to see above the surface of the water.
Pin hole camera: A simple camera that demonstrates the basic principle of image formation through a tiny hole.
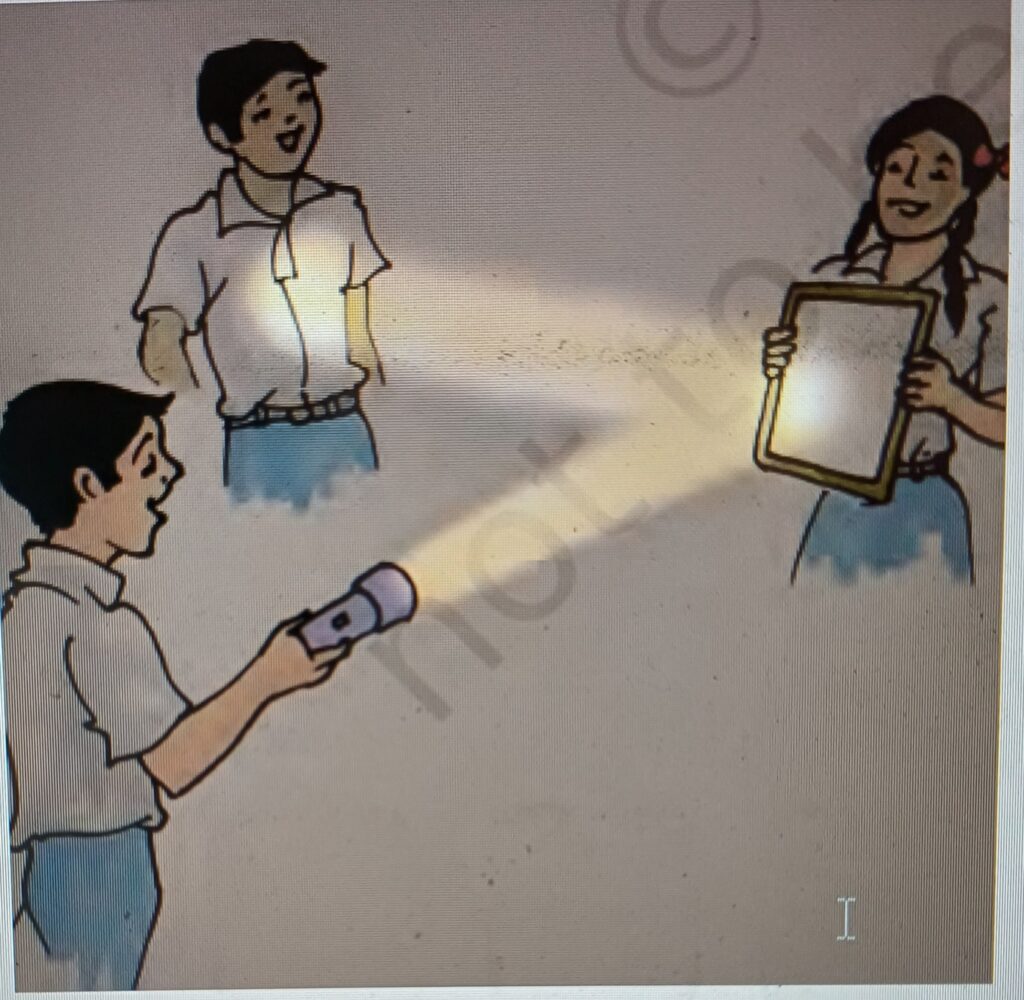
Activities and Experiments
Simple Experiments to Understand Light and Shadows
Experiment with a torch and objects: Shine a torch on different objects and observe the shadows formed.
Creating a pin hole camera: Use a cardboard box with a tiny hole to project an image onto a screen inside the box.
Observing Reflections
Experiment with mirrors: Place different objects in front of a mirror and observe the reflected images. Try using two mirrors to see multiple reflections.
Summary
Key Points
– Light travels in straight lines and is essential for vision.
– Objects can be transparent, translucent, or opaque.
– Shadows are formed when an opaque object blocks light.
– Reflection is the bouncing of light off a surface.
– Mirrors, periscopes, and pin hole cameras utilize reflection.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Common Questions About Light, Shadows, and Reflections
1. What are the sources of light?
Natural sources like the sun and artificial sources like bulbs.
2. How are shadows formed?
When an opaque object blocks the path of light.
3. What is the difference between transparent, translucent, and opaque objects?
Transparent objects allow light to pass through completely, translucent objects allow some light, and opaque objects do not allow any light to pass through.
4. What is reflection?
The bouncing of light off a surface.
Check out our easy short notes for all chapters of the Class 6 NCERT Science Book. Click here to see the full list and start learning!
